Knee Procedures
- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Partial Arthroscopic Meniscectomy
Partial arthroscopic meniscectomy is a procedure to remove the damaged part of a meniscus in the knee joint with the help an arthroscope. The meniscus is a C-shaped disc of cartilage between your thighbone and shinbone. There are 2 menisci in each knee. They act as shock absorbers and provide stability to the joint.
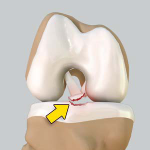
Saucerization
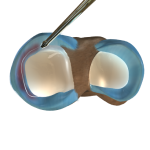
Saucerization is a surgical procedure performed to treat a discoid (disc-shaped) meniscus in the knee joint which is more prone to injury. The normal meniscus is crescent-shaped cartilage cushioning the ends of the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone) in the knee. There are two menisci in each knee, one on either side. During saucerization, the abnormally thick discoid meniscus is cut and re-shaped into a crescent.
Matrix Induced Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (MACI)
Matrix-Induced autologous chondrocyte implantation is an innovative, FDA-approved cartilage restoration procedure that uses your own cells to repair cartilage defects in your knee. It can alleviate knee pain, help you regain function and may even delay or prevent arthritis.
Arthroscopic Debridement
Arthroscopic debridement or a clean-up is a surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope. In this procedure, the cartilage or the bone that is damaged is removed using surgical instruments and the edges of the articular cartilage that are rough will be smoothened. A washout or joint lavage is done using a special tool to spray jets of fluid to wash and suck out to remove the remaining debris around the joint.
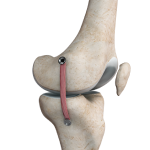
Failed Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
The knee joint is stabilized by four strong ligaments. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) passes diagonally in the middle of the knee, ensuring that the thigh and shin bone do not slide out of alignment during movement. ACL injury is one of the most common sports injuries of the knee joint and is generally repaired with ACL reconstruction surgery, where the torn ligament is replaced with a graft tendon. While this process is a very common and highly successful procedure, some may fail to achieve stability.
Failed Meniscus Repair
Meniscal repair may be performed either by open surgery under direct vision or minimally invasively using an arthroscope, which is a thin tube fitted with a camera that can be inserted into the knee through a very small incision to locate and repair the damaged meniscus.
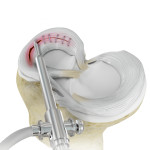
Meniscal Transplantation
Meniscal transplantation is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged meniscus of the knee with healthy cartilage. The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage ring that acts as a cushion between the shinbone and the thighbone. Each of your knees has two menisci - one on the inside (medial aspect) and the other on the outside (lateral aspect)of your knee. Apart from the cushioning effect, the menisci also provide stability to the knee.
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy is a surgical procedure indicated in individuals with torn meniscus where the conservative treatments are a failure to relieve the pain and other symptoms. Meniscectomy is recommended based on the ability of meniscus to heal, patient’s age, health status, and activity level. The meniscus is the C-shaped two pieces of cartilage located between thighbone and shin bone that act as shock absorbers and cushion the joints. Meniscus distributes the body weight uniformly across the joint and avoids the pressure on any one part of the joint and development of arthritis. Being the weight-bearing part, the meniscus is prone to wear and tear and meniscal tear is one of the common knee injuries. Meniscal tear may be developed by people of all ages and is more common in individuals who play contact sports.
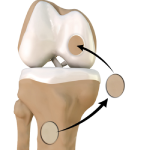
Mosaicplasty
Weight-bearing joints, such as the knee, may develop defects in the articular cartilage (spongy tissue that lines and cushions joints during movement) due to stress, trauma or degenerative disease. This can lead to pain, swelling or locking at the joint. Mosaicplasty is a surgical technique to repair the defect by transplanting healthy bone and cartilage from non-weight bearing areas of the knee. It is indicated to treat small cartilage defects of less than 2 cm in young active adults less than 45 years of age.
Posterolateral Corner Reconstruction
Posterolateral corner injury is damage or injury to the structures of the posterolateral corner. The structures of the posterolateral corner include the lateral collateral ligament, the popliteus tendon, and the popliteo-fibular ligament. Injuries to the posterolateral corner most often occur with athletic trauma, motor-vehicle accidents, and falls. An isolated injury to the posterolateral corner is rare but often occurs with injuries to the cruciate ligaments, the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Prior Meniscectomy
The menisci are two C-shaped cartilages that act as shock absorbers between the thigh and shin bones that articulate at the knee joint. They provide stability and lubrication to the joint as well as nutrition for the articular cartilage. Tears in the meniscus may occur as a result of acute injury or chronic degeneration with age. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and catching or locking of the joint. Meniscus tears can be surgically treated by meniscectomy.
Quadriceps Tendon Repair
Quadriceps tendon is a thick tissue located at the top of the kneecap. The quadriceps tendon works together with the quadriceps muscles to allow us to straighten our leg. The quadriceps muscles are the muscles located in front of the thigh.
Tibial Eminence Fracture
The tibia or shin bone is a major bone of the leg which connects the knee to the ankle. A fracture or break in the upper part of the tibia is known as a proximal tibial fracture and commonly occurs just below the knee joint. The knee joint is the largest weight-bearing joint of the body, where the lower end of the femur or thigh bone articulates with the tibial plateau. The upper fourth of the tibia constitutes the proximal part and is composed of cancellous bone. By nature, cancellous bone easily undergoes compression and depression, following an injury.
Chondroplasty
Chondroplasty is a surgical procedure to repair and reshape damaged cartilage in a joint. The procedure involves smoothing degenerative cartilage and trimming any unstable flaps of cartilage.
Physeal Sparing Reconstruction of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Physeal sparing reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament is a surgery to replace a torn anterior cruciate ligament or ACL, a major ligament of the knee, while minimizing damage to the growth plate (physis) present near the end of the bone. Ligaments are powerful bands of tissue that attach one bone to another, and the anterior cruciate ligament attaches the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia) to help stabilize the knee joint.
Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone (BPTB) Autograft
An autograft refers to using organ or tissue (bone, cartilage, tendon or skin) from the same person to transplant elsewhere on their body. ACL reconstruction with BPTP autograft is a surgical procedure that replaces the injured ACL with an autograft containing patellar tendon and bony attachments. The new ACL is harvested from the patellar tendon that connects the bottom of the kneecap (patella) to the top of the shinbone (tibia). The goal of the surgery is to tighten your knee and to restore its stability.
Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone (BPTB) Allograft
An allograft is an organ or tissue such as bone, cartilage, tendon or skin, taken from one person (donor) and surgically placed in another person to repair damaged tissue. ACL reconstruction with BPTP allograft is a surgical procedure that replaces the injured ACL with an allograft containing patellar tendon and bony attachments. The goal of the surgery is to tighten your knee and to restore its stability.
Hamstring Autograft
An autograft refers to using organ or tissue (bone, cartilage, tendon or skin) from the same person to transplant elsewhere on their body. ACL reconstruction with hamstring autograft method is a surgical procedure to replace the torn ACL with part of the hamstring tendon taken from your leg. The goal of ACL reconstruction surgery is to tighten your knee and restore its stability. The Hamstring is the muscle located on the back of your thigh. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Hamstring Allograft
An allograft is an organ or tissue such as bone, cartilage, tendon or skin, taken from one person (donor) and surgically placed in another person to repair damaged tissue. ACL reconstruction hamstring allograft method is a surgical procedure to replace the torn ACL with hamstring allograft. The goal of ACL reconstruction surgery is to tighten your knee and restore its stability.
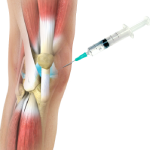
Viscosupplementation
Viscosupplementation refers to the injection of a hyaluronan preparation into the joint. Hyaluronan is a natural substance present in the joint fluid that assists in lubrication. It allows the smooth movement of the cartilage-covered articulating surfaces of the joint.
Physical Therapy for Knee
Physical therapy is an exercise program that helps you to improve movement, relieve pain, encourage blood flow for faster healing, and restore your physical function and fitness level. It can be prescribed as an individual treatment program or combined with other treatments. It involves a combination of education, manual therapy, exercises and techniques such as water, heat, cold, electrical stimulation and ultrasound.
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to diagnose or treat a knee problem. It is a relatively safe procedure and you will usually be discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery.
Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy
Tibial tubercle osteotomy is a surgical procedure that is performed along with other procedures to treat patellar instability, patellofemoral pain, and osteoarthritis. The tibial tubercle transfer technique involves realignment of the tibial tubercle (a bump in the front of the shinbone) such that the kneecap (patella) traverses in the center of the femoral groove. The patellar maltracking is corrected by moving the tibial tubercle medially, towards the inside of the leg. This removes the load off the painful portions of the kneecap and reduces pain.
Multiligament Reconstruction of the Knee
Multiligament knee reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair or replace two or more damaged ligaments of the knee joint. The surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques.
Patellar Tendon Repair
Patella tendon rupture is the rupture of the tendon that connects the patella (kneecap) to the top portion of the tibia (shinbone). The patellar tendon works together with the quadriceps muscle and the quadriceps tendon to allow your knee to straighten out.
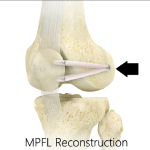
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
The medial patellofemoral ligament is a band of tissue that extends from the femoral medial epicondyle to the superior aspect of the patella. It is a major ligament that stabilizes the patella and helps in preventing patellar subluxation (partial dislocation) or dislocation.
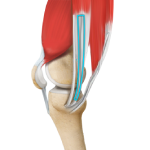
Arthroscopic Reconstruction of the Knee for Ligament Injuries
The surgical repair of the completely torn ligament involves reconstruction of the torn ligament using a tissue graft taken from another part of the body or from a donor. The damaged ligament is replaced by the graft and fixed to the femur and tibia using metallic screws. Gradually, over a period of a few months, the graft heals. Arthroscopic reconstruction of the knee ligament is a minimally invasive surgery performed through a few tiny incisions. An arthroscope is inserted into the knee joint through one of the small incisions to provide clear images of the surgical area (inside the knee) to your surgeon on a television monitor. Guided by these images your surgeon performs the surgery using small surgical instruments inserted through the other small incisions around the knee.
PCL Reconstruction
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), one of four major ligaments of the knee, is situated at the back of the knee. It connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). The PCL limits the backward motion of the shinbone.
LCL Reconstruction
The knee is the largest joint of the body and is stabilized by a set of ligaments. In the knee, there are four primary ligaments viz. anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a thin set of tissues present on the outer side of the knee, connecting the thighbone (femur) to the fibula (bone of the lower leg). It provides stability as well as limits the sidewise rotation of the knee.
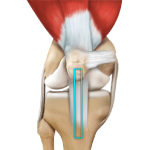
ACL Reconstruction
ACL reconstruction is a commonly performed surgical procedure. With recent advances in arthroscopic surgery, it can now be performed with minimal incision and low complication rates. The advancements in arthroscopic surgery make it easy for surgeons to view and work on knee structures through small incisions. The repair of the torn ligament can be performed at the same time as the diagnostic arthroscopy with fewer surgical risks.
ACL Reconstruction of Patellar Tendon
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction patellar tendon is a surgical procedure that replaces the injured ACL with a patellar tendon. The goal of ACL reconstruction surgery is to tighten your knee and to restore its stability.
ACL Reconstruction Procedure of Hamstring Tendon
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the major stabilizing ligaments in the knee. It is a strong rope-like structure located in the center of the knee running from the femur to the tibia. When this ligament tears, it does not heal on its own and often leads to the feeling of instability in the knee.
MCL Reconstruction
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is one of four major ligaments of the knee that connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone). It is present on the inside of the knee joint and helps stabilize the knee.
Cartilage Replacement
Cartilage replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace the worn-out cartilage with new cartilage.
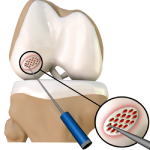
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation
Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) is a procedure to treat the articular cartilage defects of the knee. This procedure is effective for treating small areas of cartilage damage that causes pain and swelling and restricts range of motion. Autologous chondrocyte implantation is not indicated if you have advanced arthritis of the knee.
Partial Meniscectomy
Partial meniscectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the torn portion of the meniscus from the knee joint.
Meniscal Surgery
Two wedge-shaped cartilage pieces are present between the thighbone and shinbone. These are called menisci. They stabilize the knee joint and act as shock absorbers.
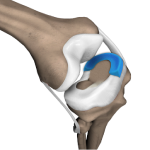
Partial Lateral Knee Replacement
Partial lateral knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the lateral part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement. The knee is one of the largest and complex joints in your body. The joint is connected to your thigh bones and bones of the lower leg by various ligaments. The knee joint is made of three compartments. The lateral, the medial and the patellofemoral compartment. The outside part of the knee is the lateral compartment. It consists of a Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL).
Transphyseal Surgery
Surgery may be necessary to reconstruct an irreparable anterior cruciate ligament (torn ACL). It usually involves the use of a soft tissue graft which is passed through tunnels drilled into the shin and thigh bones and secured to these bones. In a child or adolescent, a transphyseal surgery may be performed where the tunnels pass through the growth plate or physis (area near the end of a long bone where growth is still occurring). Injury to this area could potentially affect growth and result in deformity. An appropriate surgical technique is used to minimize these effects.
Partial Transphyseal Surgery
Partial transphyseal surgery is an arthroscopically assisted operative procedure to reconstruct the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee of a child or adolescent with growth plates or physis (areas near the ends of long bones where growth is still occurring). Reconstruction of the ACL is performed using a soft tissue graft which is passed through tunnels drilled into the shinbone (tibia) and thighbone (femur) and secured to these bones. Partial transphyseal surgery is performed to minimize injury to the physis which could potentially affect growth and result in deformity. The tunnel is created such that it passes centrally through the physis of the tibia while sparing the physis of the femur.
Non-Surgical Knee Treatments
The knee is a complex joint which consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that make joint movements easy and at the same time it is more susceptible to various kinds of injuries. Knee problems may arise if any of these structures get injured by overuse or suddenly during sports activities. Injuries to the knee can be caused by degenerative diseases such as arthritis, traumatic injuries, and sports injuries. These conditions may affect the bones & joints and impair the mobility as well as the quality of life of the patients.
Physical Examination of the Knee
A complete physical examination of the knee is performed when you present to your doctor with a knee complaint. Both of your knees are examined and the results of the injured knee are compared to those of the healthy knee.
Pre-op and Post-op Knee Guidelines
Planning for your knee surgery prepares you for the operation and helps to ensure a smooth surgery and easier recovery. Here are certain pre-operative and post-operative guidelines which will help you prepare for knee surgery.
Am I a Candidate for Knee Surgery?
Arthritis of the knee can cause pain and stiffness, making regular activities such as walking and bending difficult. As arthritis progresses, conservative treatments tend to lose their efficacy and more definitive treatment should be considered. Knee replacement surgery involves replacing worn or damaged joints with implants to reduce pain and improve movement. It provides excellent results for many and is usually performed on those above 60 but may also benefit young patients with certain conditions.
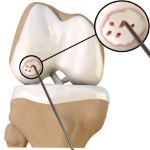
Cartilage Repair
The articular surfaces of the body’s joints are lined by hyaline cartilage, a smooth tissue that serves as a shock absorber and allows easy movement of the bones within the joint. Normal wear-and-tear or injury can damage and cause defects in the cartilage, resulting in irregular articular surfaces that interfere with movement, causing pain, swelling and disability.